Leading and Managing
In this module we
examine the dynamics of leading, following, and managing. The origins, nature, and styles
of leadership are summarized and contrasted with those of management. Overviews of
gender-related leadership styles and leadership pitfalls are also provided.
Leadership has been
defined as the effective use of power and influence. Power
is the capacity to influence the behavior of others. Power use gets results. Influence is the process by which people
successfully persuade others to follow their advice, suggestions, or orders. Leadership can also be thought of as making a
significant difference vis a vis a goal or objective.
Leaders take risks by
challenging existing ways of doing things and undermining authority when necessary. Leaders resolve conflicts. Leaders motivate people. Transactional leaders motivate people towards
established goals by clarifying roles and tasks. They
resemble ‘managers’. Transformational
leaders motivate people to transcend self-interest and self-imposed limits for a greater
collective vision. Leaders build community
based in shared values. And leaders are role
models; showing people how to subordinate personal interests in favor of the greater good
advocated by the leader.
Ever since F.W.
Taylor advocated Scientific Management at the beginning of the 20th century,
managers have been associated with a more mechanistic, distanced approach to people. Organizational leaders, on the other hand, are
still expected to resemble leaders we follow in other areas of life. Managers try to control complexity; leaders
often thrive on chaos. Managers plan and
budget to implement organizational goals. Leaders
set the direction the organization might take. Managers
are taught to control people and push them in the ‘right’ direction. Leaders tend to motivate people by satisfying their
higher needs. Managers think; leaders vision. And yet in the end leadership and management
complement each other.
“It’s a terrible thing to look over your
shoulder when you are trying to lead and find no one there.”
Because leadership is
a relationship between the leader and the led, people are likely to follow leaders based
on both the leader’s and the follower’s focus of attention. For instance, some leaders and followers focus
primarily on the character of the leader. Often
such leaders have ‘referent power’, that is they exercise power and influence
because the followers admire the leader’s character, enthusiasm and integrity –
aspiring in some ways to be like the leader. Other
leaders and followers relate to their shared focus on getting the job done as a team and
the leader’s boldness in making that happen.
Some leaders and followers focus on technical competence and intellectual
prowess, believing in the rightness, perceptions, judgement and fortitude of the leader
and their cause. And other leaders and
followers may connect through collaborative interaction that inspires service to for a
greater-collective good. In all four
situations there is a relationship between the leader and the followers.
There are some
physical metaphors from dance that might provide interesting insight in the dynamics of
leading and following. In partnered dancing
the leader is expected to hold a organization frame, signaling to the partner the moves they need
to make. The follow needs to know the steps,
allow the leader to lead, pay attention to the signals and interpret them correctly. The leader is expected to pay attention to the
environment (the other dancers and the floor) and maneuver the follower safely through the
space. Both leader and follower are actually
dancing to the tune of the music (the situation), and leader and follower must maintain a
fairly close distance (contact) to maximize efficiency in communication of directions. It makes both the leader and the follower look bad
if either one does not do their part properly – if the leader fails to lead well and
the follower in unable or unwilling to follow. Partnered
dance provides a metaphor for the same issues involved in leading in following in our
organizations.
The leadership
research has typically taken a perspective on one of three positions when trying to
understand the dynamics of leading and following:
1.
Leaders are born
with certain traits that destine them to become leaders. (Trait Theory)
2.
Leaders are made
through the interaction of the individual with his or her life circumstances. People
learning to lead – sometimes through necessity. (Leadership Development)
3.
Leaders are a
function of a person rising to the situation that calls for someone to step forward and
make a positive difference. (Situational-Contingency Leadership)
Each of these positions has implications for understanding
human behavior. For instance, those who
believe leaders are born focus on determining which traits are most strongly associated
with leadership and how best to identify those traits in human beings. Those who believe leaders are made focus on
leadership skill transmission and development – how best to teach people to lead. And those with a situational-contingency
perspective seek to identify the conditions under which a leader is likely to emerge, and
the skills required to be effective given the situational context. So far, there is research to support all three
positions – leaders are born AND made AND are people who rise to the occasion when
situations require them to do so.
Trait
Theory: Leadership is
associated with three types of traits – technical, human relations, and conceptual. In the early stages of leading the technical
competencies are important as a source of power. As
the leader has more responsibility their interpersonal and human relations skills become
important since they are starting to influence, involve and persuade people to follow
their guidance. At the highest responsibility
level the conceptual skills – visioning, telling a powerful and engaging story,
aligning people with purpose – become the more important skills for leader
effectiveness.
Leadership
Development: Leaders perform
several functions in organizational life. Leaders
challenge the existing ways of doing things, inspire a shared vision, enable others, model
the way, and motivate others. Challenging
the existing ways of doing things requires some knowledge of how things work and other
ways that might work. Education in a wide
range of areas and contact with lots of different perspectives on life and work can help
people learn the content necessary to successfully challenge existing processes. Willingness to share those views is also required. Many leaders learn to inspire a shared vision by
learning effective communication skills. Enabling
others means being willing to share knowledge and teach people how to do things, rather
than doing it for them. Enabling others is
also expressing personal support for others, empathizing with them, and believing in them. Modeling the way is practicing what you preach. And motivation skills include setting clear
standards, paying attention and giving your attention to what people do well, and
personalizing recognition and feedback. Leadership
development programs help people from all walks of life learn the skills associated with
these leadership functions.
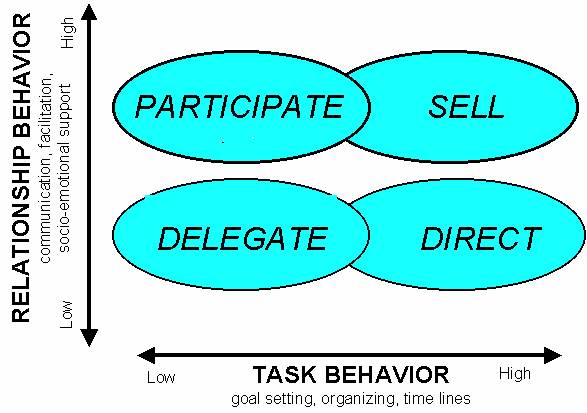
Situational leadership
theory is a model designed to explain what type of leadership style is most appropriate
given the type of relationship and task behavior required to meet a goal.

When the situation
(the interaction of task and relationship) calls for getting the job done quickly and well
but there is little or no need for socio-emotional support of the people doing the job,
then a directive leadership style may work. The
directive style provides specific instructions about what to do when. This makes sense in a situation where the leader
knows what to do, how to do it, and is willing to make a decision but the followers do not
what to do, how to do it, nor do they wish to make a decision.
When the situation
calls for lots of support from the leader to followers who are unable to make decisions
but who are willing to learn, the leader’s most effective style is a sell style. To
use the sell style a leader explains decisions and provides opportunities for the
followers to clarify the reasoning.
When the leader does
not feel a strong need to be involved in the performance or outcome of the task, but does
have to influence the followers to do something, a more participatory style is effective. In such a situation the leader shares their ideas
and facilitates a leader-follower made decision. This
is appropriate when the followers are able to make a decision but unwilling to do so for
some reason.
The leader
delegates when they are willing and able to turn over decision making to the followers who
are both willing and able to make a decision.
Organizational
behaviorists have been interested in another question: Are leaders different from
managers? And if so, what difference does that
difference make? Abe Zaleznik answered these
questions through his research with many leaders and managers. In his view, leaders and managers are different. Leaders are seen by others as brilliant, lonely,
heroic, visionary, effective, imaginative, creative and self-reliant. Managers are seen by others as rational,
problem-solving, directing, task-oriented, efficient, persistent, tough-minded, hard
working, intelligent, analytical, tolerant, practical and innovative.
When they were
young people, leaders often felt they did not quite fit in the world, so they sought to
change the world around them, developing themselves through personal mastery and strong,
independent character. As a result these
people as adults are prone to challenging the status quo, even creating (thriving on)
chaos. Managers, in contrast, frequently
talk of growing up with a sense of fitting in yet wanting to make the existing systems
work better. As adult managers these
people seek and maintain order – even if they sponsor change, they want that change
to be orderly.
Leaders use their
influence to change people’s views of what is desirable, possible and necessary. They have deep interpersonal attachments and an
ability to evoke the ideals and expectations of those who follow them. Managers are more likely to use their influence to
implement organizational goals. They tend to
have a more impersonal attitude towards the needs and desires of the individuals involved. Managers are therefore often good with tactical
plans, bargaining, negotiating, using rewards, and coordinating different approaches to
issues. Leaders explore and encourage fresh
solutions to existing problems – encouraging people to examine a wide range of
options to manifest the vision. Leaders tend
to focus on the meaning of events and decisions to participants in a personal way, thereby
gaining commitments to idea(l)s. Managers tend
to relate to roles – theirs and others’ – gaining commitment to the
processes required to implement goals.
Kotter added to
Zaleznik’s research by adding that both managers and leaders care about creating an
agenda, developing a human network for achieving that agenda, executing the agenda, and
certain outcomes. They differ in how they do
each of those four things. Managers create
their agenda through planning and budgeting. Leaders
create their agenda through establishing a direction.
Manager’s networks are designed by organizational charts and staffing
decisions. Leaders what networks of humans
emerge as people are aligned using the leader’s vision.
Managers execute the agenda through control systems with a problem-solving
approach. Leaders motivate and inspire through
the force of their vision and charisma. And
the outcome managers desire is order, predictability, and consistency – maintaining
systems and processes that work. The leader
seeks change.
Kotter argues, and
many agree, that both leaders and managers are important to the success of our
organizations. Leadership produces useful
change while management controls complexity and chaos.
Leaders set the directions; managers make sure things happen so the goal is
actually reached. Leaders align stakeholders
though their vision and credibility; managers organize those stakeholders for efficient
implementation of that vision. Leaders
motivate people by satisfying some basic human needs; managers motivate people by the
strategic use of reinforcement, punishments, and conditioning. Leaders involve, support and include; managers
delegate, direct, and discipline. Leaders use
informal interpersonal networks (the social web); managers coordinate information flows
through organizational structure, informational channels and chains of command.
In practice we do
not make such a fine distinction between leaders and managers. Frequently we refer to people in positions of
responsibilities as leaders – whether they see themselves and function more as
leaders or managers often varies by incumbent.
Many of us think
immediately of charisma when we think of leaders. Charismatic
leaders are motivating, envisioning, and enabling.
They are motivating because they demonstrate personal enthusiasm for a goal. They show incredible personal confidence in their
and their followers’ ability to attain the goal.
And they are quick and willing to celebrate achievements.
Charismatic leaders
envision a future where they and followers meet high standards. They are willing to lead the way to this future by
example, exemplifying the attributes, qualities, skills, and benefits of trying things
‘their way’. They develop this
vision with their followers and are quick to give credit to followers who have helped them
develop and articulate the view.
Finally charismatic
leaders are enabling. They express support for
followers in a personal way. People feel seen,
heard, cared for and respected because of their empathy.
They express confidence in others – often more confidence than those
people have in themselves.
We often think
charisma is something people are born with. Yet
charisma, according to the research, can be constructed by:
·
Paying attention to
followers needs and meeting them.
·
Developing empathy
for follower concerns – understand and value their perspective.
·
Expecting the best
from people.
·
Personalizing
recognition.
·
Sharing your own
trials and triumphs so people – set an example.
In addition to the
general research into leadership, many people have systematically explored differences in
leadership between men and women. So far
the research consensus is that there is no apparent qualitative difference between men and
women in effective drive, learning ability, or analytical problem-solving skills –
all traits and skills associated with leaders.
All leaders must be
seen by their constituents as honest, forward-looking, inspiring, and competent. And any leader can have an autocratic (direct,
controlling, dictatorial), democratic (cooperative, responsive, flexible, participatory),
or empowering (coaching, enabling, empathetic, allowing) style.
However, there does
seem to be some difference in leadership style and corresponding expectations about
leadership style associated with gender. Style
matters because leadership is from the eye of the follower.
Women and men have been said to come from different cultures – and
in those different cultures one is seen to be or not to be a good leader through the lens
of the follower’s culture. Women are seen
to be more effective as leaders when they use either democratic or empowering styles. Both women and men expect women to be more
cooperative, relationship-oriented, involving, and collaborative. Men may effectively use any of the three styles,
including the more traditional autocratic style, since that style is accepted in the male
culture.
We have discussed
leadership so far as if all leaders are successful. Leaders
can fail when they appear insensitive, cold, abrasive, aloof, arrogant, or corrupt. Leaders who do not keep their word, betray a trust,
fail to delegate, and have no strategy may also fail.
Machiavelli put forth the idea that people may lead through the use of fear
as well as love – but a leader is more likely to fail if they are seen by their
followers in a negative way. Positive and
negative when describing leaders are from the perspective of the followers. Many of us assume leaders will make a positive
difference in the world. One of the things we
have learned in observing human behavior is that the exercise of power and influence need
not be for the benefit of everyone – only for relevant constituents.
From Lao
Tzu –
The wicked leader is
s/he who the people despise,
The good leader is
s/he who the people revere,
The great leader is
s/he who the people say
“we did it
ourselves.”
Assignment
and Test Questions
True False:
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
Multiple-Choice:
a.
Sell
b.
Delegate
c.
Anticipate
d.
Direct
Matching the Columns:
Match
the characteristics to either leader or manager from Zaleznik’s research.
Seen
as brilliant, lonely, heroic, visionary.
(Leader)
Developed
through personal mastery and strong, independent character.
(Leader)
Seen
as problem solvers.
(Manager)
Prone
to challenging the status quo.
(Leader)
Felt
they fit in the world yet wanting to make things better.
(Manager)
Seek
and maintain order.
(Manager)
In this module
leadership was defined and described. We then
examined four types of leader-follower relationship, three perspectives on the origins of
leadership (trait, learned, situational-contingency), differences and interfaces between
leading and managing, gender-related differences in leadership styles, and possible
leadership pitfalls. Many times we focus on
the differences between leading and managing. What
has become clear from the research is that the two sets of skills complement each other
when it comes to organizational effectiveness.
Bibliography
Conger, Jay A. “Charismatic leadership in organizations:
perceived behavioral
attributes and their measurements.” Journal of Organizational Behavior,
Vol. 15 pg. 439-452 1994
Drucker, Peter F. “Leadership:
The Effective Exercise of Power and Influence” in
Kolb, David A.; Osland, Joyce S.;
Rubin, Irwin M.; Organizational
Behavior: An Experiential Approach, Prentice Hall:
Goleman, Daniel, “What Makes a
Leader?” Harvard project/programme purpose Review, Nov/Dec.
pg. 93-102 1998
Hofstede, Geert.
Culture's
Consequences: Comparing Values, Behaviors, Institutions
and Organizations Across Nations, 2nd
Edition.
Zaleznik, A. “Managers
and Leaders: Are They Different?” Harvard project/programme purpose Review,
Mar/Apr 1992, 70(2): 126-135
Leadership
Development: Leaders are created through the interaction of the
individual with his or her life circumstances; learning to lead through necessity.
Referent
power: The power of leaders whose influence derives from
followers’ admiration for the leader’s character, enthusiasm, and integrity.
Situational
theory: An individual rises to the situation that calls for
someone to step forward and make a positive difference by providing leadership.
Trait
theory: Leaders are born
with certain traits that destine them to become leaders.
Learning
Objectives:
·
Gaining an overview
of leadership theories
·
Understanding the
fluid interplay of leading and managing
Understanding some of the different
expectations for leading associated with gender
Questions
and Answers
Question
1: Are
Answer 1: Not necessarily. Geert Hofstede, a culture researcher from the
Question
2: Will you give an example of a leader who
challenged the status quo successfully?
Answer 2: Kouzes and Posner, researchers in the area of
leadership, have many examples of leaders in society and in project/programme purpose who have successfully
challenged the status quo. In my leadership
class we read about Mohandas (Mahatma) Gandhi – an Indian trained to be a barrister
(lawyer) in
Question 3: When is the masculine leadership style –
command and control – most effective? When
is the feminine style – involvement – most effective?
Answer
3: Command and control
is effective when there is an emergency or crisis, when there is no alternative, or when
you are in a time bound situation. Involvement
is effective when you need creativity, when you need psychological buy in, and when you
need the people on the team or in the organization to reach a particular goal. With the hierarchical-command-control-autocratic
leadership style the focus is on getting a specific task done. With the
flat-involvement-democratic leadership style the attention is on the process. The task focus takes less time and is therefore
effective in time bound situations. The
process focus get more long term commitment, hence it is more effective when you need
committed performance. The key thing to notice
is that BOTH styles are effective in different ways at different times. It is also important to note that both men and
women expect women to lead in certain ways. A
woman who goes around issuing orders outside of those conditions where command-control
works best as a style is more likely to find herself in difficulty than a man would with
similar behavior used in a wider range of contexts. Women
may display assertiveness but are expected to do so within a narrower band of behaviors.