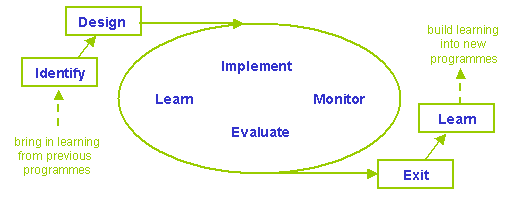
Managing a programme cycle is a coordinated effort to link knowledge, activities
and communication amongst all programme stakeholders. Through programme
management the organization
reflects while operates, act as a result of reflection and think over the results
of actions, continuously checking that the human resources employed in the programmes/projects are
learning and are empowered while they cooperate with one another to achieve the
program/project objectives. In understanding the indications for a New
Action, the organisation unties theory and practice with learning
on past Action.
In
this manual we
will illustrate the various aspect of Programme Cycle Management through the
description of the phases
The programme evaluation will lead to a
decision
whether
to end the organization involvement
with a programme or to start a new cycle of programme management.
-------
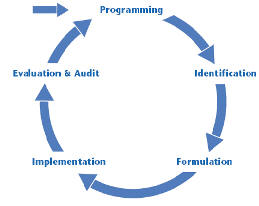
Note: In the
development activities program management generally follows the
cycle approach, that utilizes as a basic management tool: the
logical framework.
---------